Types of Procedures
Clean Procedures (Orthopedica/Breast) - Cefazolin to cover staph and strep.
Procedures involving bowel anerobes (gram neg-bacilli, enterococci) - Cefoxitin +/- metronidazole (for resistant aerobic gram neg bacilli e.g. E coli).
Craniotomies - Ceftriaxone for good CSF penetration.
Procedures with groin incisions (vascular surgery, hysterectomy, colorectal) - Add gentamicin, ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin or aztreonam for gram-neg bacteria.
Timing of prophylaxis
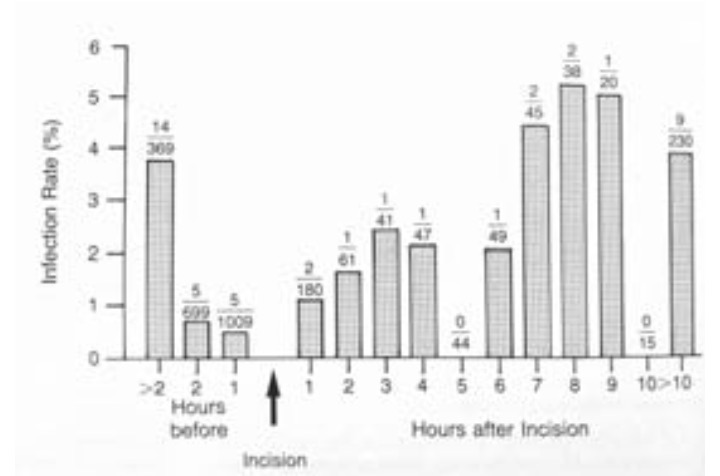
- Antibiotic therapy should be given within 60 min prir to surgical incision for adequate serum drug tissue levels at incision.
Rates of surgical wound infection (number of infections/number of patients) vs. time of antibiotic administration:
Administration
Antibiotics should be given via a slow infusion:
Vancomycin - Over 30-60 min to avoid Red Man Syndrome
Gentamicin - Over 30-60 min to avoid ototoxicity/nephrotoxicity.
Metronidazole - over 60 minutes
Ciprofloxacin - over 30 minutes
Clindamycin - over 10-15 minutes
Ertapenem - over 30 minutes
Common doses
- Ampilcillin 1 g
- Cefazolin 1-2 g (2g for patients >80kg)
- Cefoxitin 1-2 g
- Clindamycin* 600-900 mg
- Gentamicin* 1.5 mg/kg
- Metronidazole 500 mg
- Zosyn 3.375g
- Ceftriaxone 1g
- Vancomycin 1g
Ciprofloxacin 400mg
can potentiate neuromuscular blockers.
Allergies
True incidence of allergy in patients with a history of penicllin allergy <10%. Only IgE-mediated reaction (type 1, immediate hypersensitivity) are true allergic reactions.
Cross reaction between penicillin and cephalosporins <<< 10%
For penicillin allergic patients, consider vancomycin or clindamycin +/- (ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, gentamicin, or aztreonam for gram negative coverage).
Allergic reactions are more likely from neuromuscular blockers than antibiotics.