1. Discuss the pharmacokinetics of propofol?
Pharmacokinetics:
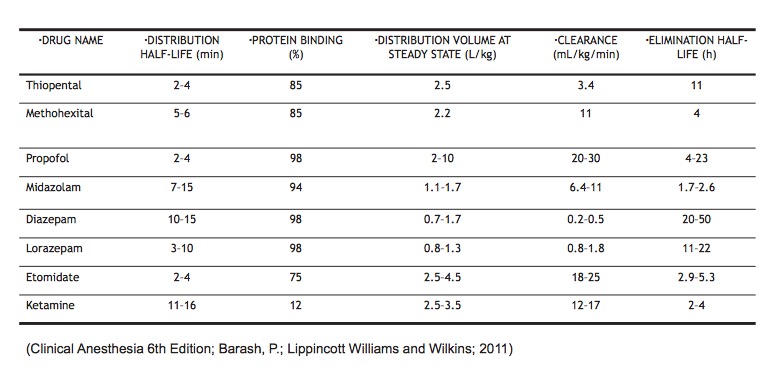
Special Circumstances:
- Children require higher doses (as they have larger Vd and higher clearance).
- Elderly require lower doses (as they have small Vd and decreased clearance).
2. What are the effects of propofol in the different organ systems?
- Neuro: Decreases cerebral metabolic O2 requirements, cerebral blood flow, intracranial pressure.
- CV: Decreases SVR, direct myocardial depressant.
- Pulm: Dose dependent respiratory depression (apnea in 25-35% of patients).
3. How is it used clinically?
- Induction 2 mg/kg
- Sedation ~75 mcg/kg/min
- Hypnosis ~200 mcg/kg/min
- Also used to prevent post-op nausea/vomiting in high risk cases.
4. What is the mechanism of action of benzodiazepines?
Increase frequency of Chloride channel opening, thereby increasing the efficiency of GABA-receptor and chloride ion channel coupling.
5. What are the effects of benzodiazepines on the respiratory system and the central nervous system?
- Neuro: Decreases Cerebral Oxygen Requirements (CMRO2), Cerebral Blood Flow (CBF), and Intracranial Pressure (ICP) .
- CV: Decreases SVR and BP.
- Respiratory: Causes dose-dependent respiratory depression.
6. What are the clinical uses of benzodiazepine?
Anxiolysis, amnesia, sedative, hypnosis, anticonvulsant.
7. What is used to reverse benzodiazepines?
Flumazenil is a specific antagonist. Very short acting (~1 hr of action). May see re-sedation as benzodiazepine is eliminated more slowly compared to effects of flumazenil.
8. What class of drugs does ketamine belong to?
NMDA Antagonist
8. What is the mechanism of action of ketamine?
Produces a dissociative anesthetic state with profound analgesia and amnesia despite maintenance of consciousness.
Used for sedation, chronic pain patients.
9. What are its effects on the various organ systems?
- Neuro: Increases cerebral metabolic O2 requirements (CMRO2), Cerebral Blood Flow (CBF) and Intracranial Pressure (ICP). Contraindicated in neurosurgical procedures.
- CV: Cardio-stimulating effects 2/2 direct sympathetic stimulation (negatively affects myocardial supply-demand), but intrinsic myocardial depressant.
- Respiratory: Minimal respiratory depression; Bronchodilation: Protects Airway Reflexes; Increased secretions.
10. What are the clinical uses of etomidate?
Sedation when hemodynamic stability is required. This is because etomidate does not induce histamine release like the other IV anesthetics do.
11. What are the effects of etomidate on the different organ systems?
- Neuro: Decreases cerebral metabolic O2 requirements, cerebral blood flow, intracranial pressure.
- CV: Maintains hemodynamic stability (minimal cardiac depression as no histamine released)
- Respiratory: Minimal respiratory depression as no histamine released.
12. What are the side effects of etomidate?
Myoclonus, pain on injection, inhibits adrenocortical synthetic function, PONV.
13. What class of drugs does dexmedetomidine belong to?
Selective α2 adrenergic agonist.
14. What are the effects on the cardiovascular and respiratory system?
CV: Bradycardia, heart block, hypotension. Respiratory: Minimal effects (does not cause significant respiratory depression unlike other inhaled anesthetics).
14. How is it used clinically?
Hypnotic, Analgesic. Used as an adjunct in general anesthesia to reduce opioid requirements without causing respiratory depression. Can also be used for sedation during awake fiberoptic intubations.
15. Clinical Cases
In the following clinical scenarios, what anesthetics would you use and why?
70 yo male with well controlled hypertension and CAD, presenting for elective colectomy.
Propofol: Reliable induction and elimination, acceptable side effects. Elective colectomy is also a long procedure which will require significant analgesia, so propofol's anti-nausea properties will be an asset.
25 yo male, mentally challenged, agitated, no IV access for dental rehab.
Consider inhalation induction with sevoflurane or using IM midazolam first.
42 yo previously healthy male in burn unit for lower extremity dressing change.
Ketamine because it is cardiostimulating (a benefit in burn patients who may be volume depleted), offers excellent analgesia, and induces a dissociative state.
30 yo multigravid female for emergency C-section 2/2 bleeding placenta previa, BP: 80/40.
Etomidate as it has minimal cardiac depressive effects and is safe in pregnancy. Ketamine can also be considered as it also offers good analgesia.
27 yo intoxicated male in ER, s/p MVA, combative, unable to obtain vital signs because of agitation.
Benzodiazepines as they are anxiolytic, reduce psychomotor agitation and offer protection against alcohol withdrawal.